Zigbee Hub
4. Zigbee Hub
4.1 What is Zigbee Hub in SLZB-OS?
The Zigbee Hub feature allows the SLZB device to run its Zigbee network directly on the device — without needing an external computer, Raspberry Pi, or NAS to host the Zigbee stack.
In Zigbee Hub mode, SLZB-OS launches an integrated Zigbee stack service that can connect directly to your smart home platform over MQTT.
This mode is ideal for:
-
Self-contained setups where the device acts as both the coordinator and the host.
-
Reducing complexity by eliminating extra hardware.
-
PoE/Ethernet-based installations for maximum stability.
When Zigbee Hub is active, a dedicated Zigbee Hub menu appears in the SLZB-OS interface, containing the following pages:
-
Dashboard – Live overview of Zigbee network status.
-
Devices – List and manage all paired Zigbee devices.
-
MQTT – Configure the MQTT broker connection.
-
Settings – Advanced Zigbee network and coordinator options.
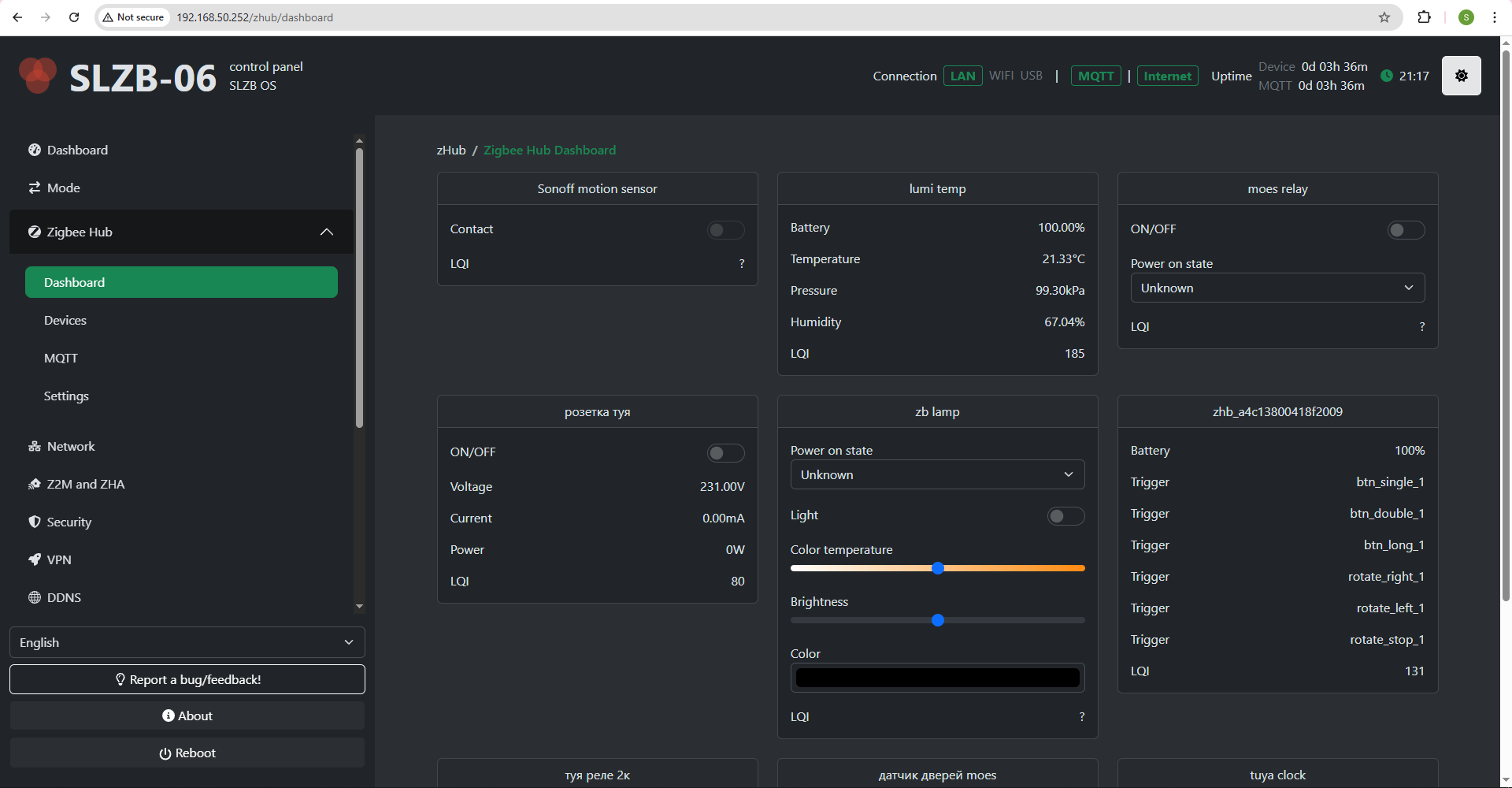
4.2 Zigbee Hub → Dashboard
The Dashboard is the central monitoring page for your Zigbee network.
The dashboard contains cards of your ZigBee devices with the data they provide and controls.
The dashboard is updated in real time via SSE.
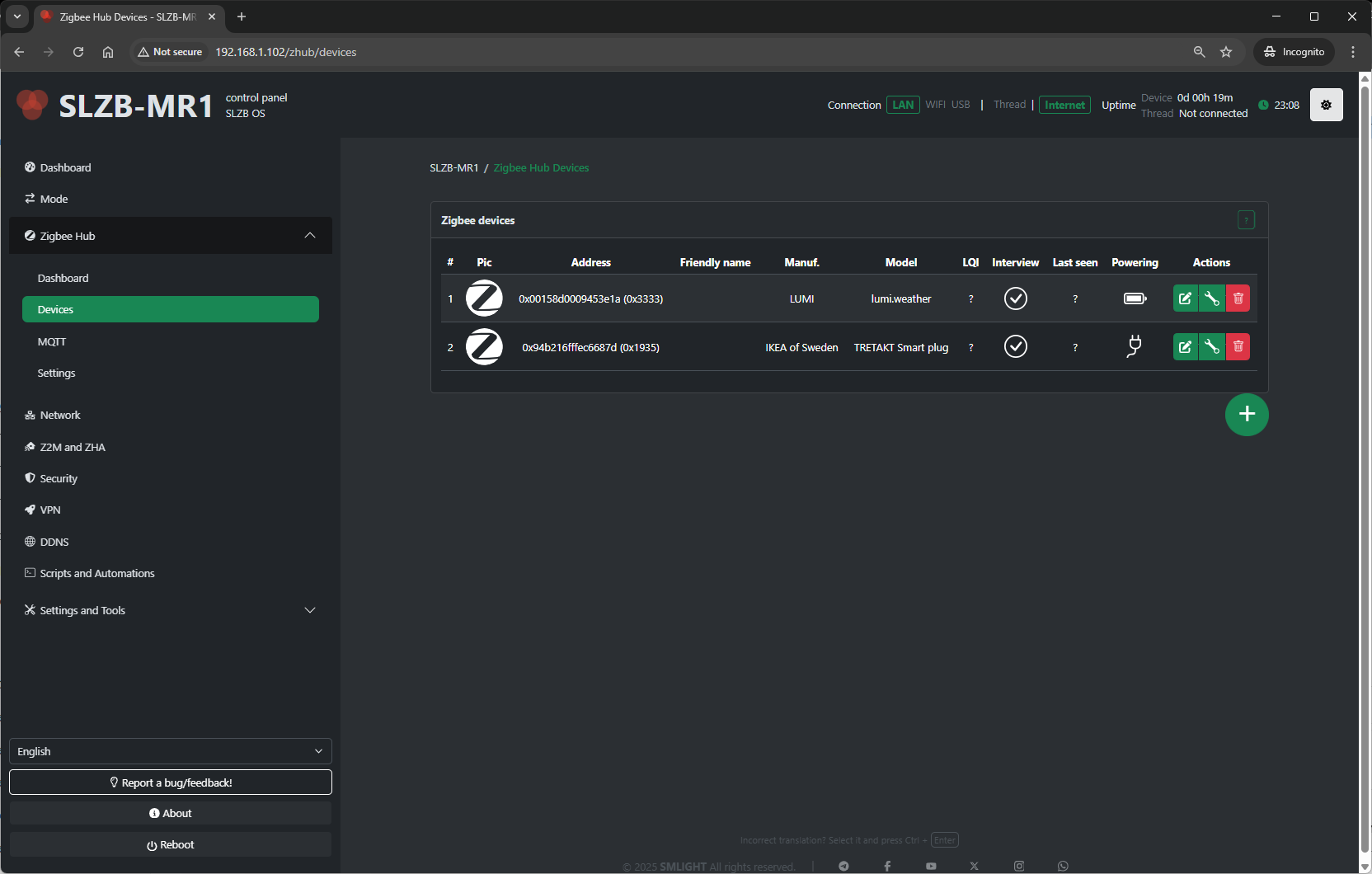
4.3 Zigbee Hub → Devices
The Devices page lists every Zigbee device paired to your coordinator.
Pairing control:
- Permit Join (+ button on the bottom right side of the device table) – Allow or deny new devices joining the network.
For each device, you’ll see:
-
Name / Friendly Name – Human-readable identifier.
-
IEEE Address – Unique device ID.
-
Network Address – Short Zigbee address assigned by the coordinator.
-
Last Seen – Timestamp of the last communication.
- Powering – Device power source (AC/battery) or ? if the device does not provide information.
-
Link Quality (LQI) – Signal strength indicator.
-
Actions:
-
Rename device
-
Remove/unpair device
-
View device details (clusters, endpoints, bindings)
-
Bind/unbind devices (if supported)
-
Typical uses:
-
Verify devices are online and responsive.
-
Rename devices for easier identification in automations.
-
Remove devices no longer in use.
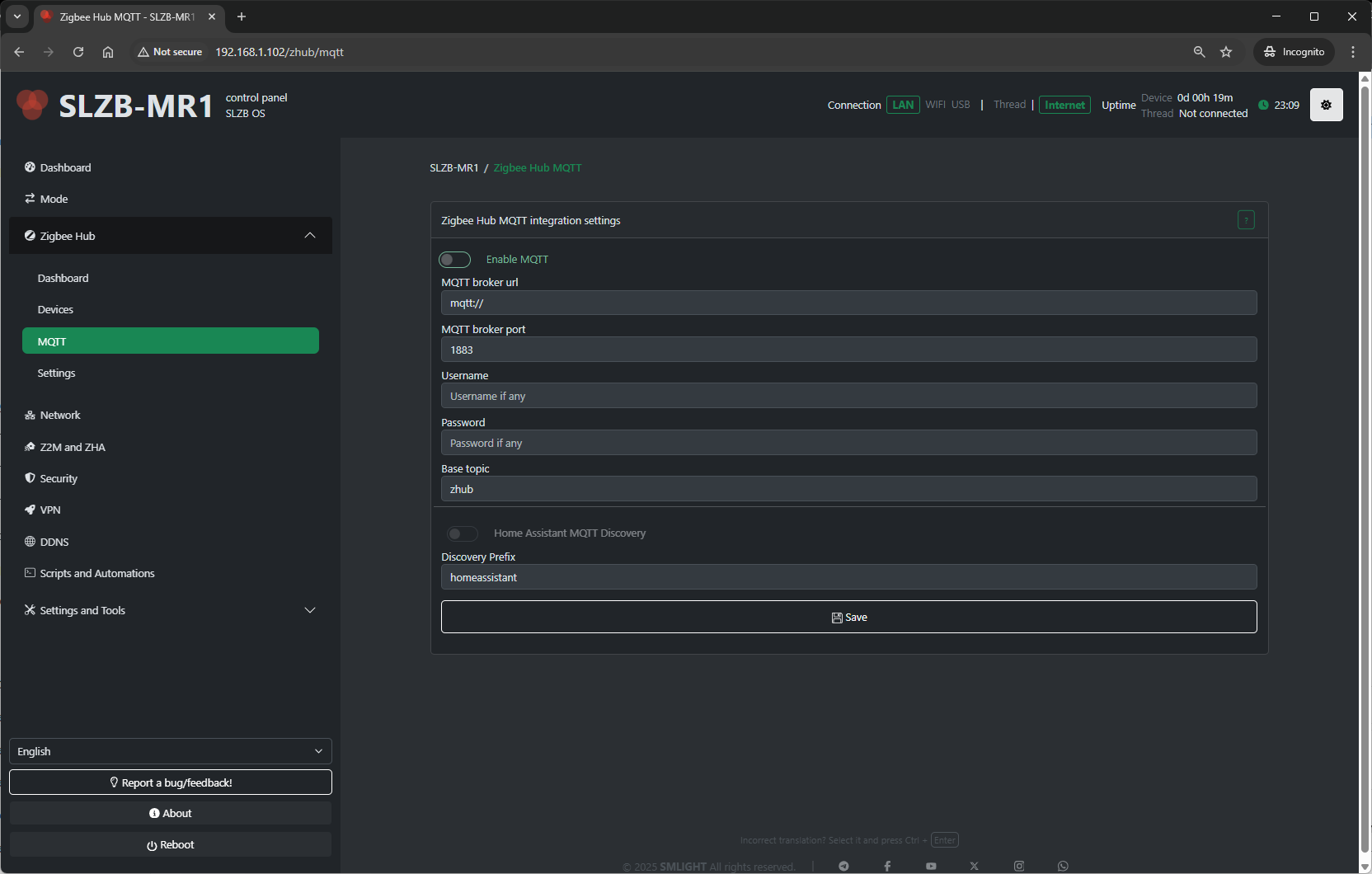
4.4 Zigbee Hub → MQTT
This page configures the MQTT connection that Zigbee2MQTT (running on SLZB-OS) uses to communicate with your smart home platform.
Configuration fields include:
-
MQTT Server Address – IP or hostname of your broker (e.g.,
mqtt://192.168.1.100). -
Port – Default 1883 for MQTT, 8883 for MQTT over TLS.
-
Username / Password – Broker authentication (if required).
-
Base Topic – Topic prefix for Zigbee messages (default:
zigbee2mqtt). - Discovery Prefix - Home assistant main topic name.
Tips:
-
For Home Assistant with Mosquitto add-on, use the HA IP and port
1883. -
Always use a unique base topic if you run multiple Zigbee networks.
-
Save and restart Zigbee Hub after making MQTT changes.
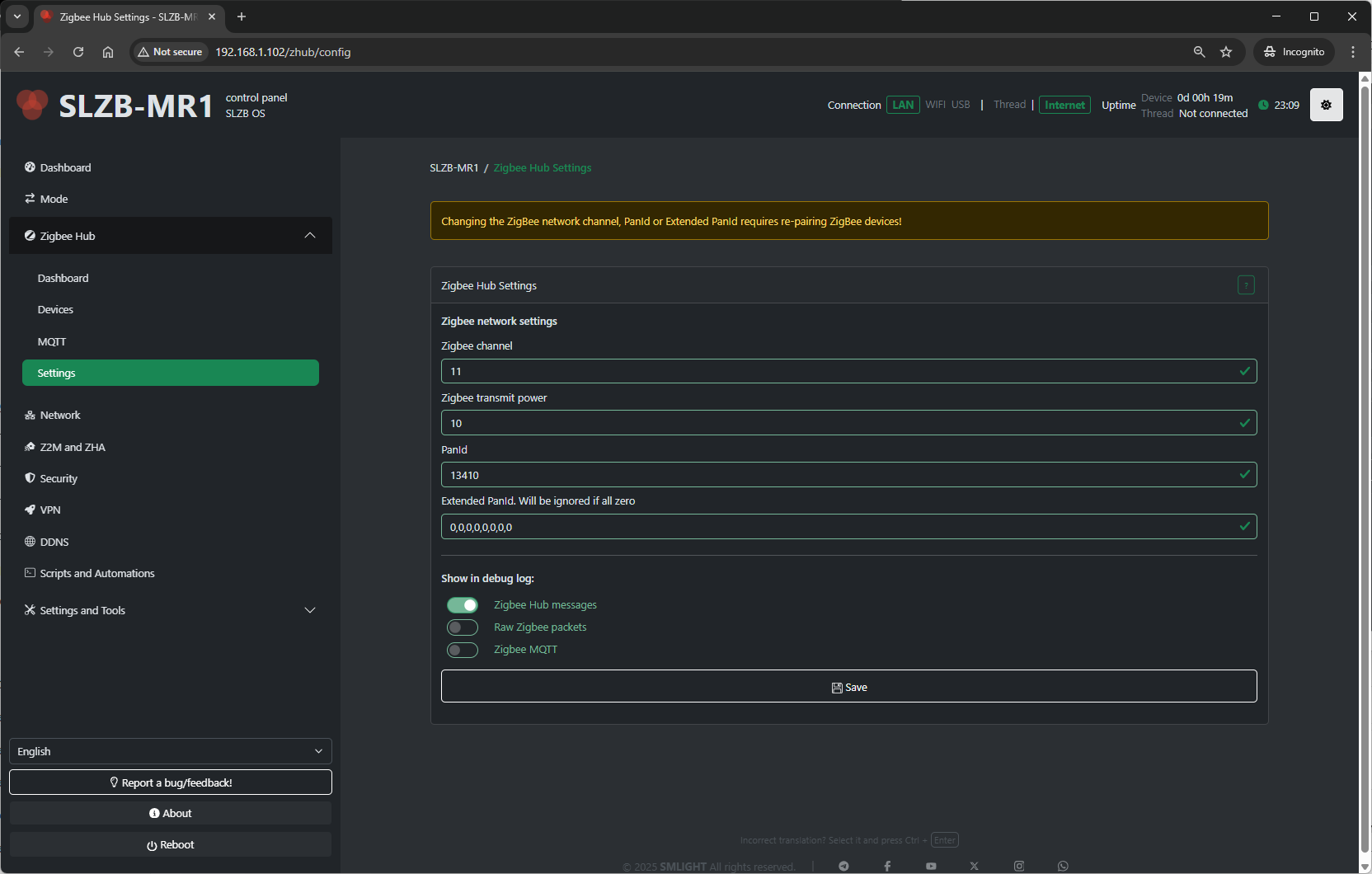
4.5 Zigbee Hub → Settings
The Settings page contains deeper configuration for the Zigbee coordinator and Zigbee2MQTT service.
Typical settings available:
-
Network Parameters:
-
PAN ID – Zigbee network identifier.
-
Channel – RF channel (11–26; avoid Wi-Fi overlap if possible).
-
Extended PAN ID – Long network identifier.
-
-
Transmit Power – Radio TX power in dBm (higher = longer range, more power draw).
- Show in debug log - Select which categories of Zigbee-related information are recorded in the Log & Debug page.
-
Zigbee Hub messages – Logs high-level events from the Zigbee Hub service (e.g., device joins, status updates).
-
Raw Zigbee packets – Logs low-level Zigbee frame data; useful for deep protocol debugging.
-
Zigbee MQTT – Logs MQTT messages related to Zigbee communication, including publishes and subscriptions.
-
Best practices:
-
Change the Zigbee channel only on a fresh network (re-pair required after change).
-
Keep
Permit Joindisabled most of the time for security. -
Adjust transmit power to match your coverage needs and regulatory limits.
4.6 Troubleshooting
Problems when starting a Zigbee network
OS v3.0.9 update is breaking. If you updated OS to v3.0.9 and started getting this error then follow the instructions below
- turn off coordinator
- turn off ALL Zigbee routers that were connected to Zigbee Hub. This is important, it will not work without this
- turn on coordinator. Zigbee Hub should start now but zigbee devices will be unavailable
- remove all devices (click on the red trash can)
- download and run berry script below, this script will keep permit join enabled as long as it is running
#META {"start":0}
#Insert your code below
import ZHB
ZHB.waitForStart(0xFF)
while 1
ZHB.permitJoin(254)
SLZB.delay(255 * 60 * 1000)
end- repair all devices
- after devices repaired you can stop and delete script
- move the coordinator away from the wifi router
- make sure there is no other coordinator nearby with the same zigbee network settings