1.What SMHUB Nano can do:
- Run Zigbee2MQTT directly on the device and connect seamlessly to Home Assistant.
- Run local automations using Node-RED, allowing logic, rules, and workflows to execute directly on the hub without cloud dependency.
- Expose Zigbee devices to Matter ecosystems, including Google Home, Apple Home, Alexa, and any Matter-enabled platform (including Home Assistant).
- Operate as a simple Zigbee coordinator (though this underutilizes the device’s full capabilities).
- Use USB devices directly on the hub or expose them to Home Assistant — for example, by connecting Z-Wave or additional Zigbee sticks for extended or mixed-protocol setups, or other USB devices such as hard drives (with the limitations disclosed in point 9).
- Install and run custom Node.js or Python applications freely (e.g., using `npm install ` or `pip install ` and freely use them).
2.SMHUB Nano basics
2.1. Access to the device
SMHUB Nano is accessed primarily through a web browser.
After connecting the device to your network (Ethernet or Wi-Fi), you simply open its IP address in a browser to reach the SMHUB web interface.
For advanced users and reviewers:
- SSH access is available for full Linux control (IP:22, auth: smlight/smlight)
- A built-in UI Console allows running commands without leaving the browser
No cloud account or vendor registration is required - everything is local.
2.2. SMHUB OS architecture (Simplified)
SMHUB Nano runs a pure Linux operating system (SMHUB-OS).
The architecture is layered:
- Linux kernel
The core of the system, responsible for stability, hardware access, and networking. System UI & backend- smhub-web – the web interface you see in the browser
- smhub-services – background services that control apps and hardware
- Applications layer
Preinstalled apps such as Zigbee2MQTT, Node-RED, Matterbridge, Mosquitto MQTT, Z-WaveJS UI, etc.
All apps run directly on the device, not in the cloud.
2.3. Updates – system and apps
Updating SMHUB Nano is straightforward and done entirely through the web interface.
- Updating SMHUB-OS (system update)
Go to Settings → System and Restore and start the system update from there. - Updating smhub-services and smhub-web
Open the Apps menu, click Refresh in the top-right corner, and then click Upgrade. - Updating other applications
Updates work the same way as for smhub-services and smhub-web. - Uninstalling applications
To remove an app, open the specific App’s pageand use the Uninstall option there.
3.Running Zigbee2MQTT with Home Assistant
Detailed manual with screenshots for Option 1 and Option 2 you can find by this link: https://smlight.tech/support/manuals/books/smhub/page/connecting-zigbee2mqtt-on-smhub-to-home-assistant
3.1. Option 1. Direct SMHUB connection: Z2M → Home Assistant
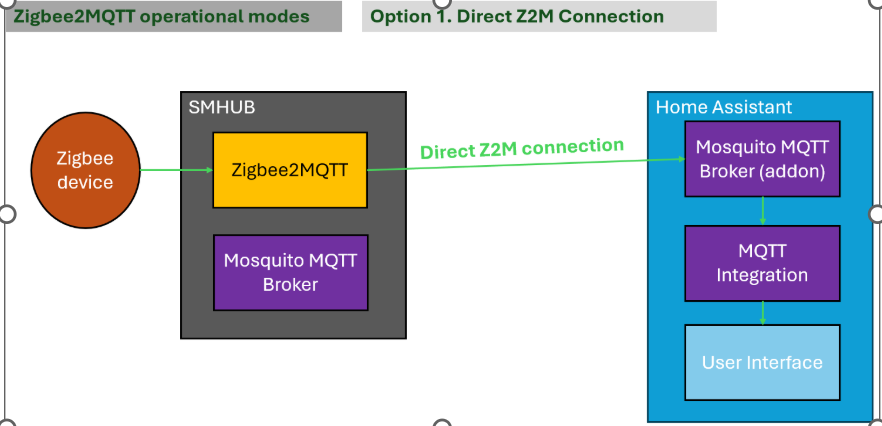
In this connection type, you run Zigbee2MQTT on SMHUB and connect it to a remote Mosquitto MQTT broker.
- Pros: fast and easy setup.
- Cons: although Zigbee2MQTT can reconnect to the MQTT broker after a connection loss, it cannot start if there is no connection to the remote Mosquitto broker.
How to connect: configure your Z2M to use Home Assistant MQTT (IP and port)
3.2. Option 2. SMHUB connection: MQTT → MQTT Home Assistant
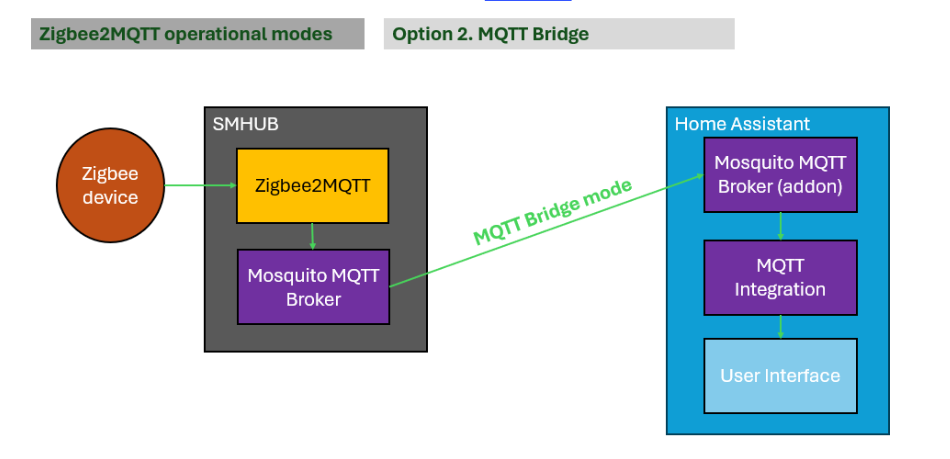
In this connection type, you run Zigbee2MQTT on SMHUB using the internal Mosquitto MQTT broker, and the SMHUB broker operates in bridge mode with Home Assistant’s MQTT broker.
- Pros: Zigbee2MQTT is practically unstoppable — it will start and reconnect under almost any circumstances. For example, even if both SMHUB and Home Assistant are rebooted, Zigbee2MQTT will still start successfully (unlike Option 1, where it would fail to start if Home Assistant is unavailable).
- Cons: Adds an extra layer of complexity (the additional MQTT broker on SMHUB) and requires extra configuration. For large systems, it is recommended to fine-tune MQTT bridge settings to reduce unnecessary traffic (for example, by bridging only specific topics instead of the full MQTT namespace).
How to connect: Set SMHUB’s MQTT broker into Bridge mode and bridge it to Home Assistant’s MQTT broker.
3.3. Option 3. Utilize only SMHUB’s radio SoC by Home Assistant
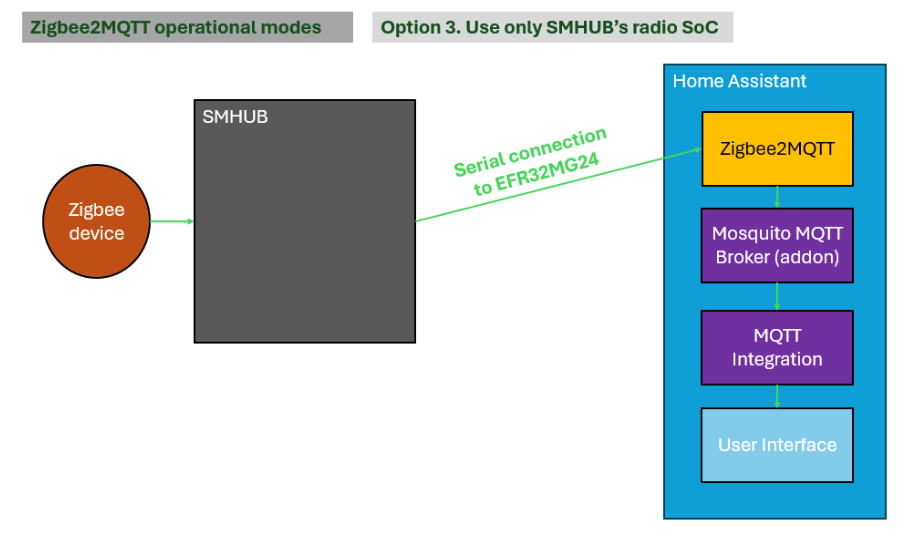
In this connection type, Zigbee2MQTT runs on Home Assistant, while SMHUB is used only as a passthrough device, exposing the Zigbee radio via serial-over-TCP.
- Pros: None. This setup does not take advantage of SMHUB’s capabilities.
- Cons: This configuration is not what SMHUB is designed for. It underutilizes the device by turning it into a simple network bridge instead of a local automation hub. Zigbee2MQTT becomes fully dependent on network availability between Home Assistant and SMHUB, which may lead to startup issues or reduced reliability compared to running Zigbee2MQTT directly on SMHUB.
4.Multidevice connection
SMHUB is designed to scale.
You can connect multiple SMHUB devices either toone Home Assistant instance or to another SMHUB, even if they are located in different networks or physical locations (for example, via WireGuard).
4.1. Connection Multiple SMHUBs to Home Assistant
Multiple SMHUB devices can be connected to a single Home Assistant instance using the same approaches described earlier (Option 1 and Option 2).
Each SMHUB runs its own Zigbee2MQTT instance and manages its own Zigbee network.
This allows you to:
- Use several SMHUBs for large homes or buildings
- Separate Zigbee networks by location or floor
- Connect remote locations securely (e.g. over WireGuard VPN)
Multiple SMHUBs → Home Assistant using Direct Z2M Connection
In this setup, each SMHUB runs Zigbee2MQTT and connects directlyto Home Assistant’s MQTT broker.
How to set this up:
- Run Zigbee2MQTT on each SMHUB
- Configure Zigbee2MQTT to use Home Assistant’s MQTT broker
- Use unique Zigbee2MQTT base topics for each SMHUB
Notes:
- Simple and clean architecture
- Requires Home Assistant’s MQTT broker to be available at startup
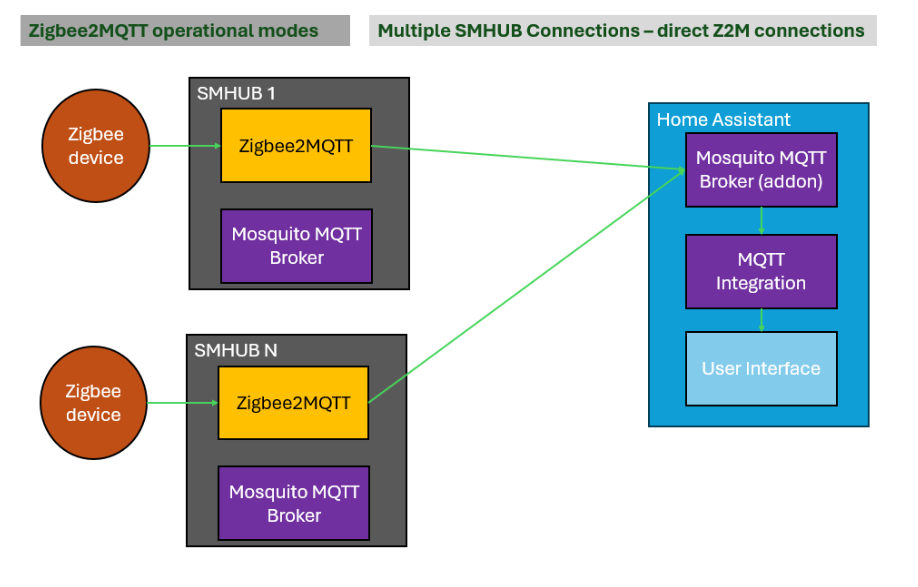
4.1.2. Multiple SMHUBs → Home Assistant using MQTT Bridge Mode
Each SMHUB runs Zigbee2MQTT using its local MQTT broker, and that broker is bridged to Home Assistant’s MQTT broker.
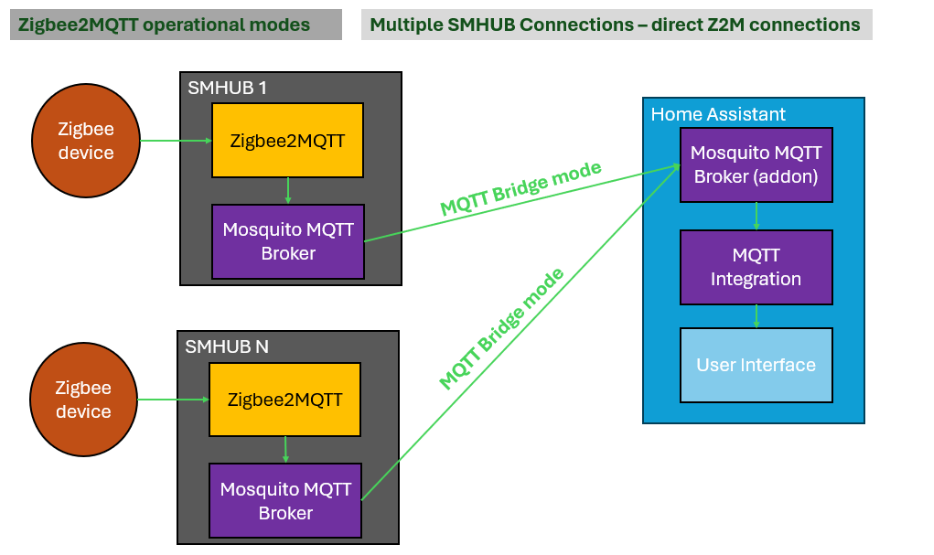
How to set this up:
- Run Zigbee2MQTT on each SMHUB using the internal Mosquitto broker
- Configure MQTT bridge from each SMHUB to Home Assistant
- Optionally filter topics to reduce traffic
Notes:
- More reliable startup behavior
- Slightly more complex initial configuration
4.2 Connecting Multiple SMHUBs to Another SMHUB
SMHUB devices can also be connected directly to another SMHUB,forming a hub-to-hub setup.
One SMHUB acts as the master, while others operate as remote hubs.
In this scenario:
- Zigbee devices connected to all SMHUBs can be controlled from one place
- Automations can run centrally using Node-RED orMatterbridge
- Useful for multi-building, multi-floor, or remote-location setups
Connection methods are the same as with Home Assistant.
4.2.1. Multiple SMHUBs → Master SMHUB using Direct Z2M Connection
Each remote SMHUB runs Zigbee2MQTT and connects directly to the master SMHUB’s MQTT broker.
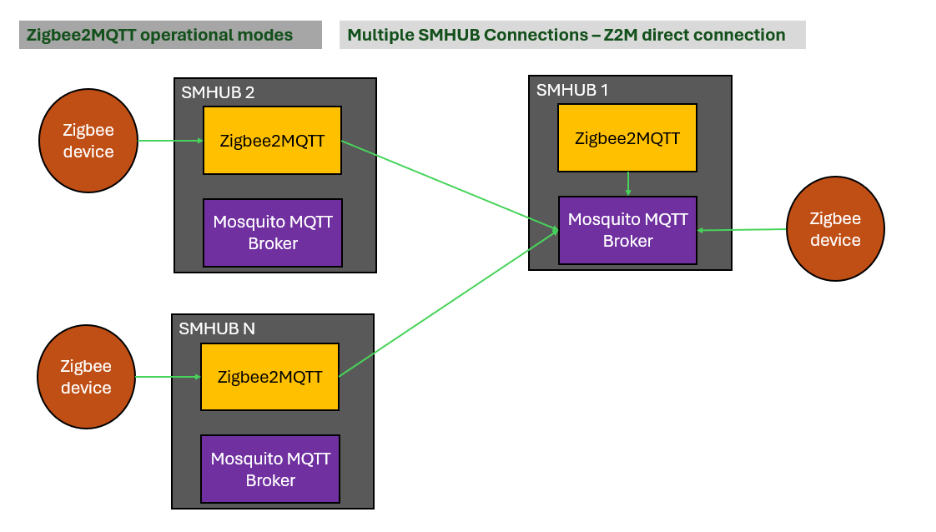
How to set this up:
- Choose one SMHUB as the master
- Configure Zigbee2MQTT on all other SMHUBs to use the master’s MQTT broker
- Note: Assign unique Zigbee2MQTT base topics per SMHUB
4.2.2. Multiple SMHUBs → Master SMHUB using MQTT Bridge Mode
Each SMHUB runs Zigbee2MQTT using its own local MQTT broker, and brokers are bridged to the master SMHUB.
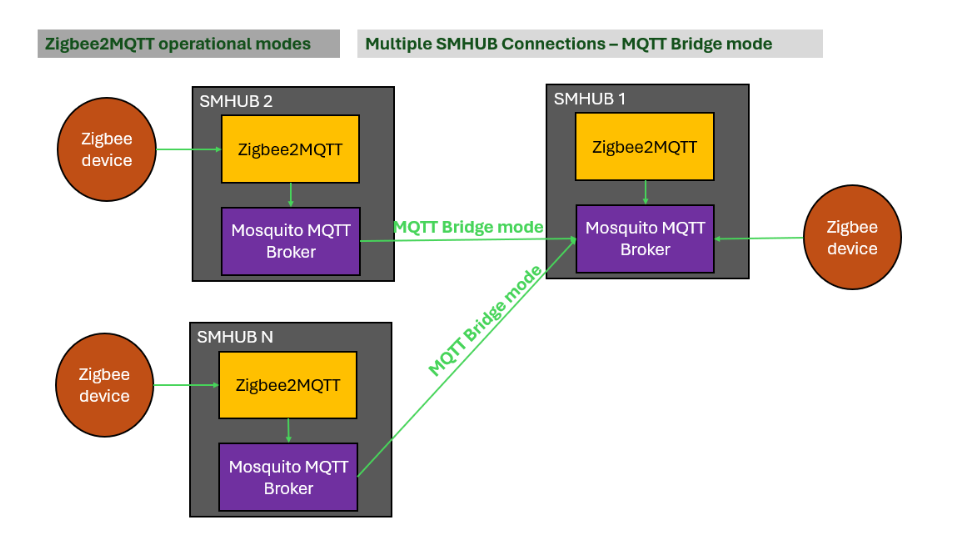
How to set this up:
- Run Zigbee2MQTT with local MQTT on all SMHUBs
- Configure MQTT bridge from each SMHUB to the master SMHUB
- Optionally limit bridged topics for better performance
Notes:
- Most resilient and scalable option
- Recommended for complex installations
5.Exposing Zigbee device from SMHUB to any Matter-enabled ecosystems via Matterbridge.
SMHUB Nano allows you to expose Zigbee devices to Matter-enabled ecosystems (such as Google Home, Apple Home, Alexa, and Home Assistant) using Matterbridge.
How It Works (Simple Explanation):
- Zigbee devices are connected to SMHUB using Zigbee2MQTT.
- Matterbridge, running directly on SMHUB, reads those devices and exposes them as Matter devices on the local network.
- Matter-enabled platforms can then discover and control these devices without direct Zigbee support.
All processing happens locally on SMHUB — no cloud services are required.
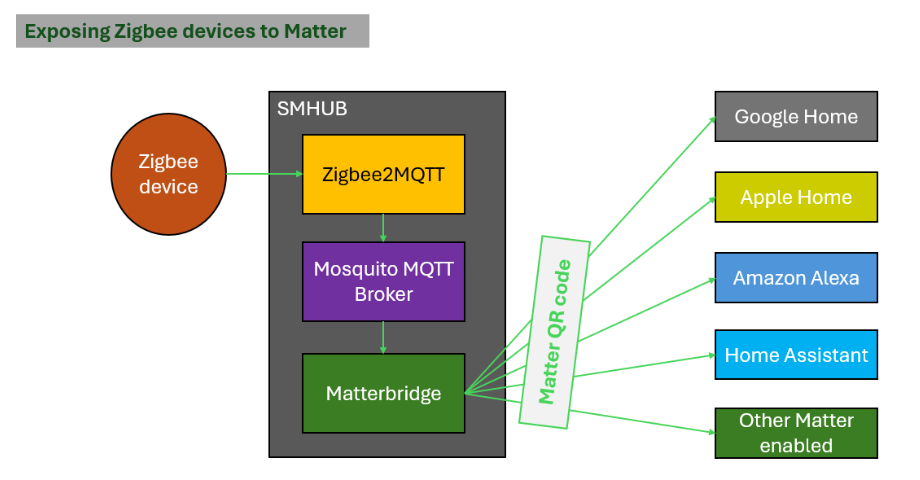
Basic Setup Steps
- Make sure Zigbee2MQTT is running and Zigbee devices are paired to SMHUB.
- Install and start Matterbridge and Matterbridge-Z2M from the Apps section in the SMHUB web UI.
- Open Matterbridge tab and see the QR code for pairing.
- Open your Matter-enabled app (Google Home, Apple Home, Home Assistant etc.) and add a new Matter device using the pairing code shown inMatterbridge.
What This Is Useful For
- Using Zigbee devices in ecosystems that normally don’t support Zigbee
- Mixing Zigbee and Matter devices in one smart-home setup
- Demonstrating cross-ecosystem compatibility in reviews
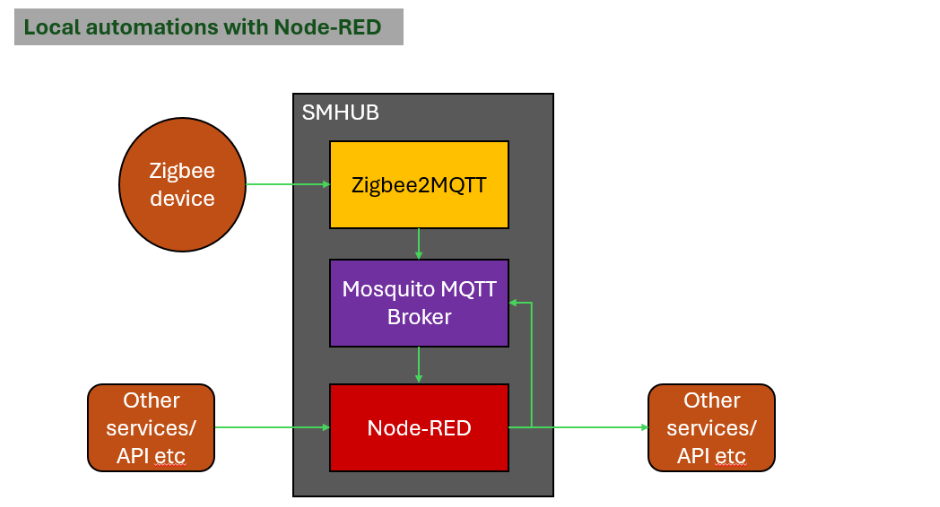
6.Local automations with Node-RED
SMHUB Nano can run Node-RED directly on the device, allowing automations to execute locally, without relying on cloud services or external servers.
How It Works (Simple Explanation):
- Node-RED runs as a local app on SMHUB.
- It can receive events from Zigbee2MQTT, MQTT, timers, or other local services and send events to Zigbee2MQTT.
- Automations (flows) are executed instantly on the hub, even if the internet is unavailable.
This makes SMHUB Nano suitable for fast, reliable, and private automation.
Basic Setup Steps
- Open the Apps section in the SMHUB web UI.
- Install and start Node-RED; from inside Node-RED, install Zigbee2MQTT “node”.
- Access the Node-RED editor from the provided web link.
- Create flows using MQTT, Zigbee2MQTT events, timers, or HTTP nodes.
What Is Useful For
- Running automations without Home Assistant
- Creating fast-response rules (lighting, sensors, buttons) – even if the network is down, rules will continue execution.
- Combining Zigbee devices, timers, and external APIs
7.Killer feature: Local Automations + Home Assistant + Proprietary (Google/Apple/Alexa)
One of the most powerful features of SMHUB Nano is its ability to combine local automation, Home Assistant, and proprietary ecosystems (Google Home, Apple Home, Alexa) into a single, coherent setup.
What Makes This Special
SMHUB Nano can act as a central automation brain, where:
- Devices are managed locally on SMHUB,
- Automations run locally (fast and cloud-independent),
- Devices are simultaneously exposed to Home Assistant and to Matter-based ecosystems.
This means you don’t have to choose between “local control” and “ecosystem compatibility” - you get both.
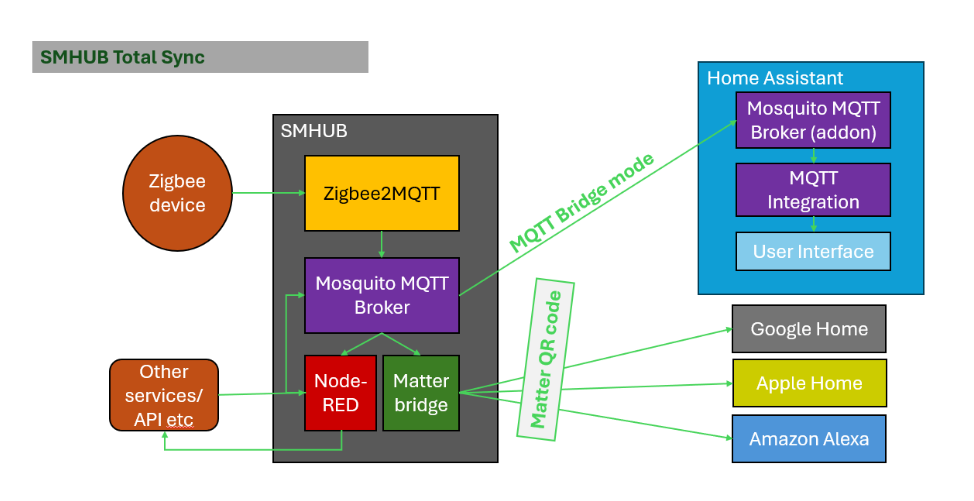
How It Works:
- Zigbee devices connect to SMHUB viaZigbee2MQTT.
- Device states are published to the local Mosquitto MQTT brokeron SMHUB.
- Node-RED uses these events to run local automations (rules, logic, workflows).
- Home Assistant connects to SMHUB via MQTT and provides dashboards, history, and integrations.
- Matterbridge, running on SMHUB, exposes selected devices to Google Home, Apple Home, and Alexa using Matter (via a QR code).
All of this happens in parallel and locally, without forcing devices to live in only one ecosystem.
Why This Is a Big Deal for Users
- Automations keep working even if Home Assistant is down
- Voice assistants and mobile apps still work via Matter
- No cloud dependency for core logic
- One Zigbee network, multiple control layers
- No duplication of devices or bridges
You can control the same light:
- via Node-RED automation,
- via Home Assistant UI,
- via Google Home / Apple Home / Alexa,
all at the same time.
8.Running Thread networks on SMHUB
SMHUB Nano can run Thread networks by acting as a Thread Border Router (OTBR), allowing Thread devices (including Matter-over-Thread devices) to communicate withHome Assistant and other IP-based systems. It directly replaces the HA Openthread Add-on, providing a more reliable and stable solution, by running OTBR directly on the device with the radio and also allowing to form Thread mesh network having multiple SMHUBsconnected to the single instance of Home Assistant.
8.1 Running a Thread Network on One SMHUB
How Thread Works on SMHUB (Simple Explanation)
- SMHUB runs the OTBR app, which bridges Thread ↔ IP networks.
- Home Assistant connects to this OTBR via the OTBR integration.
- The Thread integration in Home Assistant manages:
- Thread network creation
- Network credentials and dataset
- Pairing of Thread devices
In short:
- OTBR app on SMHUB → routes Thread traffic
- OTBR integration in Home Assistant → provides transport to OTBR
- Thread integration in Home Assistant → manages the Thread network itself
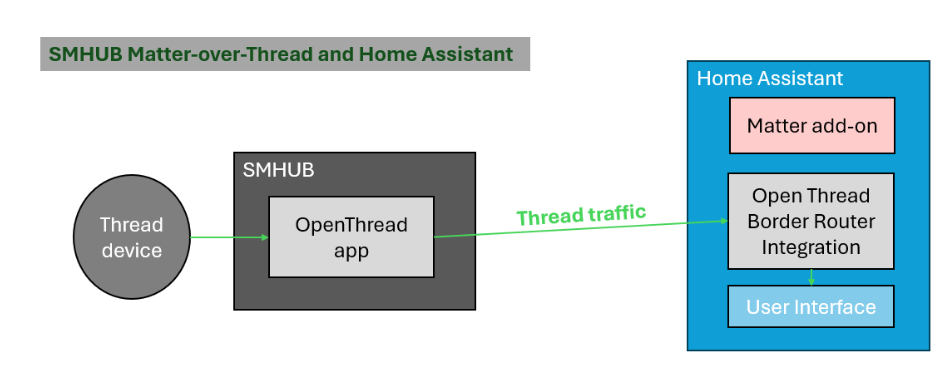
Basic Setup Flow
- Flash radio SoC to Thread network.
- Install and Start the OpenThread app on SMHUB.
- Add SMHUB to Home Assistant using the OTBR integration.
- Make sure
- Thread integration is installed (should be done automatically together with OTBR integration.)
- Matter add-on is installed and running, as it manage Matter-over-Thread behavior of Home Assistant.
- Home Assistant creates the Thread network and manages credentials.
- Pair matter-over-Thread devices using the Home Assistant app.
- After this, Thread devices become visible and controllable in Home Assistant.
Full set-up manual with screenshots is available by this link: https://smlight.tech/support/manuals/books/smhub/page/run-thread-networks
Why This Matters
- Enables Matter-over-Thread devices
- Keeps Thread routing local and fast
- Clear separation between radio routing (SMHUB) and automation/UI (Home Assistant)
8.2 Thread Mesh Network with Multiple SMHUBs
SMHUB Nano supports Thread mesh networks that span across multiple SMHUB devices, all managed by a single Home Assistant instance. Each SMHUB runs its own OpenThread Border Router (OTBR), and all of them can participate in one shared Thread network – so SMHUBs form mesh Thread network.
How This Works:
- Each SMHUB runs the OpenThread app, acting as an independent Thread Border Router.
- All SMHUBs are added to Home Assistant as separate OTBR instances to the single instance of HA’s OTBR integration.
- Home Assistant manages one common Thread network dataset and credentials.
- Thread devices connect to the nearest SMHUB, forming a single Thread mesh network.
- Thread traffic between SMHUBs is transported over the IP network, allowing border routers to cooperate even if they are not within direct radio range.
From the user’s perspective, this behaves as one logical Thread network, even though it is backed by multiple physical SMHUB devices.
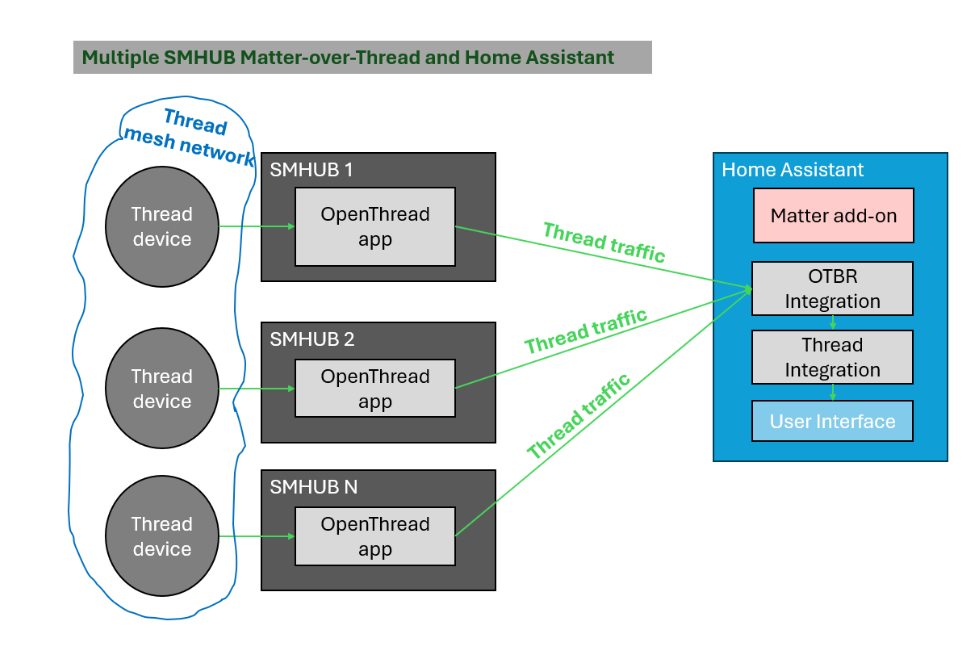
What This Enables
- Larger Thread coverage across floors, buildings, or remote locations
- Redundancy - multiple border routers improve reliability
- Scalability - add more SMHUBs as the network grows
- Single control plane - all Thread devices appear in one Home Assistant UI
Thread devices automatically communicate through the mesh and use the most optimal border router available.
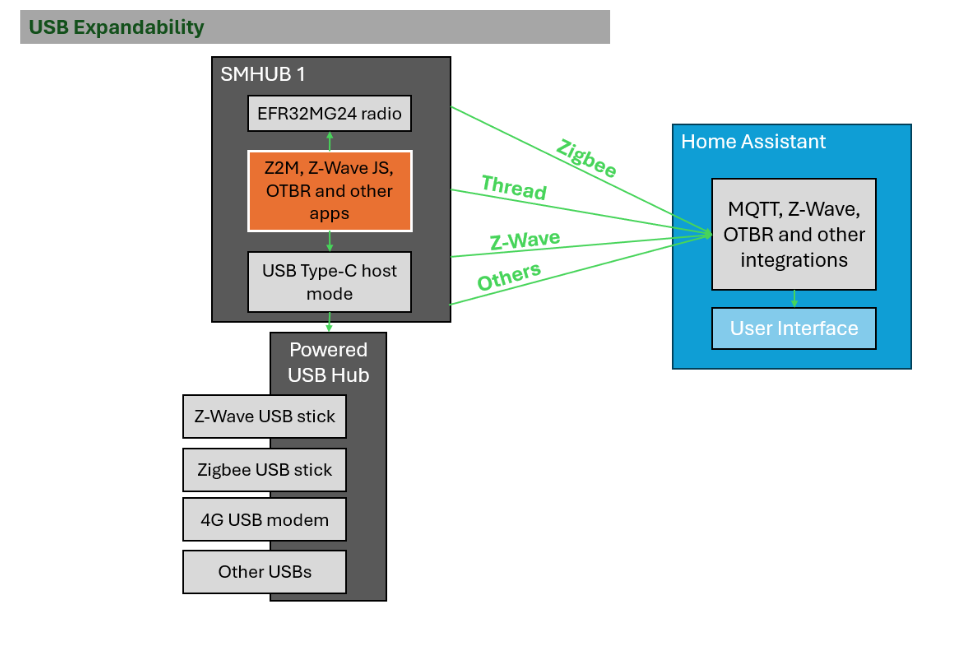
9.USB extensions for SMHUB Nano*
SMHUB Nano supports USB host mode*, allowing you to connect and use external USB devices via a powered external USB hub.
What USB Expandability Means
Once USB host mode is enabled, SMHUB can work with external USB devices such as:
- Z-Wave USB sticks
- Additional Zigbee or Thread USB sticks
- 4G/LTE USB modems
- Other USB devices (storage, adapters, sensors, etc.)
All connected USB devices are handled locally on SMHUB and can be exposed to Home Assistant through the appropriate integrations.
* USB Host mode was introduced in hardware revision 0.98, along with this documentation. You can check your hardware revision in the bottom-left corner of the web UI. It requires externally powered USB hub.
How It Works (Based on the Diagram)
- SMHUB runs local applications such as Zigbee2MQTT, Z-Wave JS, OpenThread, and others.
- Built-in radios (EFR32MG24) and USB-based radios can be used at the same time.
- USB devices are connected via a powered external USB hub attached to SMHUB’s Type-C port.
- Protocol traffic (Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread, etc.) is forwarded to Home Assistant via MQTT or native integrations.
How to Enable USB Host Mode
- Open the SMHUB web interface
- Go to Settings → USB
- Enable USB Host Mode
- Reboot SMHUB
After reboot, connected USB devices will be detected automatically.
9.1 USB Use case 1: Running Z-Wave network with ZWA-2 Z-Wave dongle on SMHUB Nano
SMHUB Nano can run a Z-Wave network locally using a USB Z-Wave dongle, such as the ZWA-2, without requiring Home Assistant to run Z-Wave network itself.
What You Need
- SMHUB Nano with USB Host Mode enabled
- Powered external USB hub
- ZWA-2 or any other Z-Wave USB dongle
- Z-Wave JS UI application installed on SMHUB
Setup Steps
- Install Z-Wave JS UI
- Open Apps in the SMHUB web interface
- Find Z-Wave JS UI and click Install
- Start Z-Wave JS UI
- Open the app and start the service
- Configure the USB Port
- Select the correct USB serial device corresponding to the ZWA-2 dongle
- Save the configuration
- Create or Join a Z-Wave Network
- Use Z-Wave JS UI to include Z-Wave devices
- The Z-Wave network now runs directly on SMHUB
Integration with Home Assistant
Once running, Z-Wave devices can be exposed to Home Assistantusing the Z-Wave JS integration, without installing Z-Wave add-ons on Home Assistant itself.
Why This Is Useful
- Runs Z-Wave locally on SMHUB
- Reduces load and complexity on Home Assistant
- Allows combining Z-Wave on one device
- Ideal for mixed-protocol smart-home setups
10.Reset and restore SMHUB
To reset your device to factory state, you can use either the Type-C flashing method or the microSD card flashing method, as described here:
https://smlight.tech/support/manuals/books/smhub/chapter/restore-and-updating
Please note that both recovery methods do not reset the radio SoC (EFR32MG24).
If the radio SoC was previously flashed, for example, as a Thread Border Router, it will remain in that state after restoring the system via Type-C or microSD.
















